Pavement dismantling on the right side of the Bridge
began 31.10.2002. As you were informed in the last Newsletter, each pavement stone has
been previously marked, documented and measured. This is a very delicate job, because the
emphasis was put on the fact that the largest possible number of these stones is to be
returned on its original place. The workers have carefully, with hand tools, separated
stone by stone, liberating it from mortar, silicon and soil.

pavment dismantling from the bridge
Pavement was then piled on wooden surface into truck, and then driven to Harem Semovac. It
was sorted there, additionally cleaned and put in previously prepared shapes.
Wooden shapes are made according to real dimensions and form of paving on the Bridge.
Nylon basis were then placed on their bottom and on top of them 10cm thick layer of sand.
This kind of basis guarantees that pavement will be conserved in the best possible way.
During pavement dismantling on the left bank we found cavity directly under the upper
layer of pavement. Cavity was formed during recent archeological excavations, because the
layer of already washed and no quality soil - simply licked out through the cavities in
the walls. System of supporting columns and beams was made even then, so the stability of
pavement was ensured at least for some time.

pavment piled on Harem Semovac
It was necessary to approach this problem very carefully because all structures of old
walls and pavement had been disturbed. Also, all dismantling work needed to be planed and
done step by step, because all of these elements were interacted and only joined together
gave relative stability of the whole structure.
It is interesting that under pavement on left side of the Bridge we found remnants of
installation – probably Austria Hungarian. That was plumbing gander pipe 20cm
diameter.
Removal of concrete
blocks
Removal of concrete blocks on both sides of the
Bridge was done from 1-16. November.
Total five blocks were broken. Three on right and two on left side of the Bridge. Great
attention was given to minimal damage of the surrounding pavement and also that
surrounding structure is not disturbed.
Archeological
excavations
Archeological excavations began after pavement
dismantling. They are conducted in a way that surface layer of soil is removed, while the
whole surface is brought to certain level. On the right bank quadrant is dug in the
dam. Until now we have reached a depth of apx. 2.5 m below the surface of pavement.
Remnants of three walls were found, and they were examined, documented and has digging
continued. Dam that is dug out is removed by crane.

quadrant on the right bank
Left side is explored only to a depth of 0.8m, because here excavations are conducted in
more difficult conditions and on incomparable larger surface. Digging is done in soil,
between very weak walls, so great attention is given also to the safety of workers.
Remnants of 2 pavement layers were found here by excavations, on upstream side, in
northern profile of quadrant, directly by the edge of previous pavement of the Bridge.
First layer was found on a depth of 0.3m, with dimensions 3.5m x 2.9m, and below that the
second one, on 0.5m, 3.4m long and 2.3m wide.

quadrant on the left bank
Findings of prevoius
archeological excavations
After conducted extended but still unfinished
research works and with analysis of archive documents, development of the location can be
divided into several developing stages:
-around year 1444 towers on both sides of Neretva exist. On the right bank self-standing
semicircular tower Helebija, on the left semicircular tower Tara with six-cornered
fortification.
-before 1452 first wooden bridge was built which
connected the fortresses. The bridge was wooden with two console distinctive parts and
middle one which was “hanging”. Semicircular, unsymmetrical annex of
fortification was built for bridge reliance on the left bank, and on the right bank
trapezoid enlargement of plateau of Helebija tower with abutments of the bridge.
-between 1452 and 1566 on the right bank tower
Helebija was reinforced by sub-wall with round corridor and the crown. Tower was elevated
with wooden crown. In the same period Tara was elevated, building which served for
accommodation of the crew was built within the fortification. Year 1522 mesdzid of Sultan
Selim was constructed, smaller mosque for the crew of the fortress. South-west corner of
fortress was fortified, tower Hercegusa was constructed.
-1566 construction of builder Harjudins` bridge was finished. Distinctive flanking
abutment walls were built which reduced the span of the bridge and one-arched stone bridge
was built. Over the new entrance-gate into fortress wooden watchman tower –
“cardak” was built. Such a Tower also existed also over the gate of
fortification on the left bank.
- between 1566 and 1690, the fortification side walls were strengthened by erecting an
inner, parallel and distanced wall and filling the space between the two walls with soil.
The Tara Tower was risen once again, with a new, stone, merlon on the top. The Halebija
was also risen, with new merlin and gun holes. Between 1680 and 1695, Captain Halebija,
after who the tower was named, rebuilt it into a covered blockhouse. He rose it and opened
a number of windows, turning its uppermost floors into the crew dwellings.
- between 1690 and 1878, lesser rebuildings were made on facades, with no significant new
building. Between 1714 and 1716, lower floors of the Halebija Tower were turned into a
jail. At upper floors, the facades were modified by opening of new windows. The watchmen
corridor on the jacket wall was risen as a ramp to the northern gate. The new parapet was
built at the same time.
- buildings of the end of the 19th ct. and the 20th ct. The fish-market building at the
right bank. At the left bank, next to the bridge, a smaller storehouse. The Mesdjid was
built again on the old foundations. Between the Mesdjid and the Tara Tower, a new
residential-office building was built.
Remnants of wooden
plumbing
On the left bank, right next to north-east part of
the quadrant, wooden plumbing pipe was discovered with outer diameter 24cm and inner one
12cm. The pipe was covered with 5cm thick layer of red dirt in order to make it
water-proof.

16th centuring plumbing pipe
Outlet of Radobolja to
Neretva
This year we are witnesses of extreme high water
levels of Neretva and Radobolja. High-capacity outlet of Radobolja to Neretva was built to
allow undisturbed flow of works in those conditions.
Elements foreseen by the project were prepared and concreted on harem Semovac, and then
16th and 17th of November concreting of outlet itself was executed.
Beside outlet itself, communication over it was arranged. The road was widened and turning
point for pickup trucks was made.

concrete outlet
Repair of the abutment
walls
To begin with the grouting of abutment walls –
first important thing is to replace those stone blocks which are destroyed or damaged.
Only solid and unique wall can receive grouting mass without any problems.
Conglomerate blocks from Bisce polje quarry are being subjected to the list of tests,
which are necessary for determining their quality and compactness.
Lime
22nd of November 10 tons of lime arrived on
auxiliary site on harem Semovac. Lime was burned and extinguished in natural manner and it
is at least 12 months old.
Dismantling of remnants of parapet and cornice from the left side of the
bridge
19th of November dismantling of bridge remnants began on the left bank
of Neretva. This job is very risky because console of the bridge which remained after its
demolition, is in very ban condition. Fractures in construction are visible. The fact that
solid support for auxiliary construction still does not exist under his part of the
bridge, makes the job even harder.
First, pavement and the layer of red dirt under it were removed from the console. After
that, parapet was liberated which broke in two parts during demolition of the bridge. A
tape was dragged through beneath one part of the parapet and without any further damages
crane carried it to the platform with other blocks of the bridge.
Preparations for
erecting the centering
One of the most important elements which will influence the
reconstruction of Old bridge certainly is the centring. In the last Newsletter we
presented its construction and the main principles. In this one we are already in a
position to inform you that preparatory works for its erection are at full power.
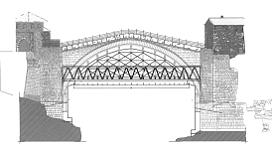
1. CONCRETING THE FOUNDATIONS
First in a row of preparatory works is concreting the foundations for heavy scaffolding.
The works have begun on the right bank of Neretva, by nailing down iron anchors 2m of
length into rocks under the bridge. Anchors are nailed down into rocks 90cm and covered
with Altex.
 |
 |
drilling of holes for
anchors |
concreting of scaffold
foundations |
Wooden bedding was erected on the rock around the anchor and concreting the layer of
liable concrete was executed.
After that, additional bedding for the foundation foot was erected on the existing one,
and reinforcement was placed inside and concreting was done again.
2.PLACING THE PONTON
In order to allow undisturbed communication
of people and material during erecting of centring, it is decided that Neretva is to be
temporarily spanned with pontoon.
Excavation, drilling and covering the anchors were done beneath feet of temporary walking
bridge. After that, planking and steel elements were erected and anchor blocks concreted
 |
 |
| anchor block on the right bank |
placing of the first pontoon element |
 |
|
| setting ponton connection |
|
Three iron ropes with diameter 15.2mm were erected and dragged through beneath the two
anchor blocks on the right and left bank. Separate ropes of pontoon elements were hooked
on the main rope with slip-knots, which allow adjusting the position of pontoon to various
water levels.
Four pontoon elements are connected with steel latticed porters over which the deck for
communication is placed